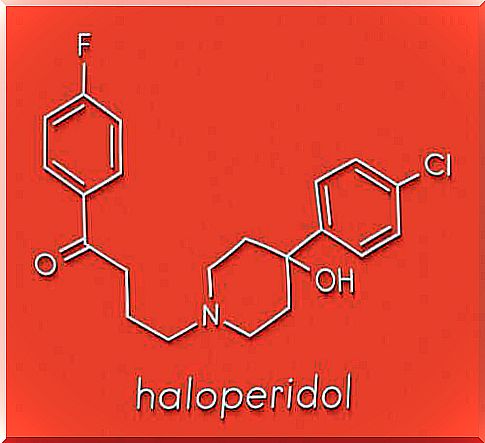
Haloperidol: What Is It And What Is It Used For?

Haloperidol is an antipsychotic or neuroleptic drug. Due to its chemical structure, it is included in the group of butyrophenones. It was discovered in 1958 by Paul Janssen. It belongs to typical antipsychotics. Therefore, it is useful in treating the positive symptoms of schizophrenia. Some of these are, for example, hallucinations, delusions and agitation.
It is a depressant agent of the central nervous system with a sedative effect. Thus, it provokes a powerful motor sedation. This effect is used to combat states of agitation and aggression.
What is haloperidol used for?
Haloperidol has many different indications in its technical file. It can be used in both adults and children. Basically, it is used as an antipsychotic in the treatment of schizophrenia and also in other psychotic and agitated states.
In people over 18 years of age, haloperidol is indicated for the treatment of:
- Schizophrenia.
- Confusional syndrome that does not respond to non-drug therapies.
- Manic episodes associated with bipolar disorder.
- Psychomotor agitation associated with psychotic disorders.
- Aggression and psychotic symptoms in patients with Alzheimer’s dementia and vascular dementia.
- Tic disorders that do not respond to other types of treatments, including Gilles de la Tourette syndrome.
- Huntington’s disease that does not respond to other treatments.
In pediatric patients, it is used since other treatments cannot be prescribed, either because they do not respond to them or because they are contraindicated. In these cases, haloperidol is indicated in:
- Schizophrenia in adolescents aged 13 to 17 years.
- Aggression in children and adolescents aged 6 to 17 years with autism or developmental disorders.
- Tic disorders, including Gilles de la Tourette syndrome, in children and adolescents aged 10 to 17 years.
In addition, the haloperidol is being studied for the prevention of delirium. Low doses of this medication seem to be useful to reduce the incidence of delirium in high-risk patients, as well as in patients who are about to undergo surgery.
Haloperidol is also used to prevent nausea and vomiting. It’s helpful against those side effects that come up after an operation, as well as those associated with chemotherapy. Several studies attest to its effectiveness and safety for this use.
Mechanism of action
Haloperidol is a potent antagonist of the dopamine. It works by non-selectively blocking central D2 receptors. It also has low antagonist activity at alpha-1 adrenergic receptors.
By blocking the dopamine pathway, its excess in the brain decreases. Thus, the haloperidol suppresses delusions and hallucinations. It also produces a certain psychomotor sedation, useful in some of its indications.
Side effects
Haloperidol, like almost all psychotropic drugs, has a number of undesirable effects. These are usually also related to the mechanism of action. In fact, the majority of adverse reactions haloperidol due to the blockade of dopamine in other systems. The most common side effects of haloperidol are:
- Extrapyramidal disorder.
- Insomnia.
- Agitation.
- Hyperkinesia.
- Headache.
Other less frequent adverse reactions that may also appear are:
- Psychotic Disorder.
- Depression.
- Weight gain.
- Tremors.
- Hypertony.
- Orthostatic hypotension.
- Dystonia.
- Somnolence.
- Urinary retention.
- Erectile dysfunction.
- Skin rashes.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Visual deterioration.

Its use is not recommended in conjunction with other antipsychotics. This is because it can increase the intensity of adverse reactions. Likewise, it can potentiate extrapyramidal effects.
A serious adverse reaction that can occur is neuroleptic malignant syndrome. It’s not very common, but it’s convenient to know it to detect it in time. It usually occurs at the beginning of treatment. It causes muscle stiffness, high fever, arrhythmia, etc. Therefore, it is important to follow the doctor’s instructions. He is responsible for controlling the treatment, as well as evaluating the effectiveness and possible risks.
Treatment should start with a low dose, which may increase depending on the patient’s response and needs, periodically evaluating the cost-benefit ratio of the treatment. Also, to avoid adverse effects, the dose should always be as low as possible.
Special care must be taken when used in elderly patients as well as children. In these cases, it is necessary to adjust the dose. Furthermore, it is necessary to observe the possible adverse effects that may appear.